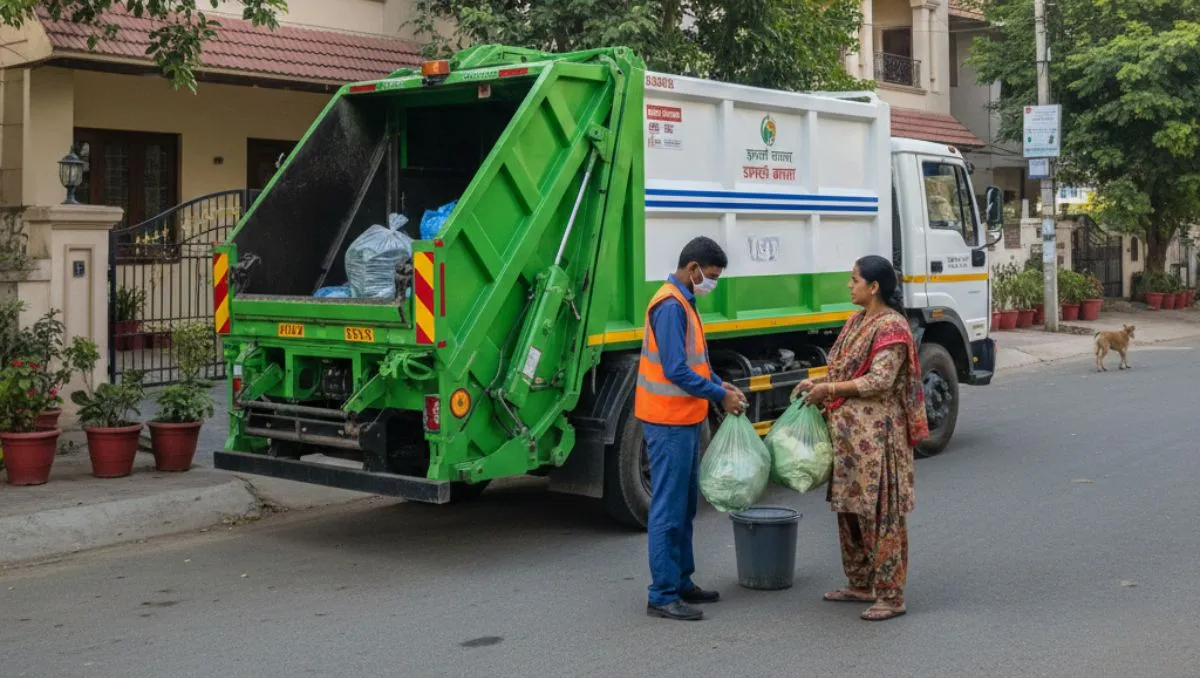
Introduction: Smart Waste Management System in IoT
In the modern era of urbanization and rapid industrial growth, managing waste efficiently has become a critical challenge for cities, industries, and municipalities alike. Traditional methods of waste collection and disposal are no longer sufficient to handle the increasing volumes of municipal, commercial, and industrial waste. This is where a Smart Waste Management System in IoT plays a transformative role, leveraging the power of the Internet of Things (IoT) to create smarter, cleaner, and more sustainable urban environments.
A Smart Waste Management System in IoT uses connected sensors, real-time monitoring devices, and data analytics to optimize the entire waste management process. From detecting when garbage bins are full to scheduling optimized collection routes for waste collection vehicles, these systems ensure operational efficiency while reducing unnecessary costs and environmental impact. The integration of IoT technology enables authorities to respond quickly to overflowing bins, prevent littering, and maintain cleaner public spaces.
Moreover, IoT-enabled smart waste systems are not just about convenience—they promote sustainability. By enabling proper segregation of recyclable, organic, and hazardous waste at the source, they support recycling initiatives and reduce the burden on landfills. Real-time analytics and predictive insights also allow municipalities to plan resources more effectively, ensuring that manpower, vehicles, and operational budgets are used efficiently.
The adoption of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT also enhances public engagement and transparency. Citizens can track waste collection schedules, report overflowing bins, and actively participate in maintaining community cleanliness through mobile applications. Additionally, the system supports regulatory compliance, helping cities and industries adhere to environmental laws while minimizing health risks associated with unmanaged waste.
With urban populations growing exponentially, the traditional approach to waste management is no longer sustainable. A Smart Waste Management System in IoT represents the future of urban cleanliness, offering a scalable, intelligent, and eco-friendly solution that combines technology, data, and community involvement to transform the way we handle waste. Cities that adopt these systems not only improve operational efficiency but also pave the way for greener, healthier, and smarter living spaces for their residents.
What is a Smart Waste Management System in IoT?
A Smart Waste Management System in IoT is an advanced solution that transforms traditional waste collection and disposal methods using the power of the Internet of Things (IoT). Unlike conventional systems that rely on fixed schedules and manual monitoring, IoT-enabled waste management integrates sensors, connected devices, real-time data analytics, and automated communication to streamline waste operations.
At its core, a Smart Waste Management System in IoT is designed to make waste collection more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable. By equipping garbage bins, dumpsters, and waste containers with smart sensors, authorities can monitor fill levels in real-time. These sensors detect when a bin is nearing capacity or if it has been tampered with, and the information is instantly transmitted to a centralized cloud platform or control center.
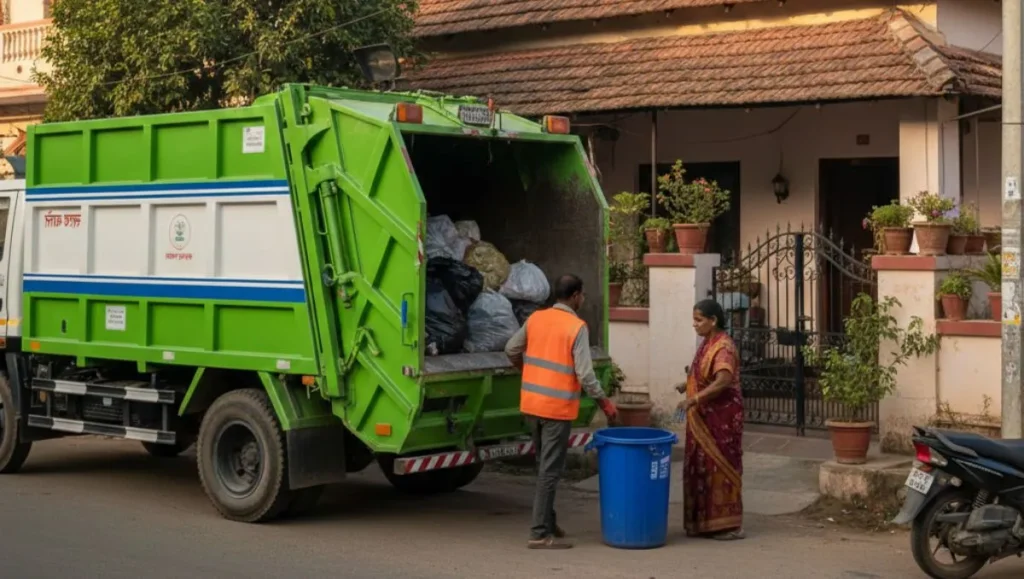

One of the key features of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT is real-time monitoring. Municipal authorities and private waste management companies no longer need to rely on manual inspections or rigid collection schedules. Instead, they can make data-driven decisions about when and where waste collection is required. This minimizes unnecessary trips, reduces fuel consumption, and lowers overall operational costs.
In addition, IoT-enabled waste management systems often incorporate smart route optimization for garbage trucks. Using GPS tracking and predictive analytics, these systems determine the most efficient routes for waste collection based on bin fill levels, traffic conditions, and geographic priorities. This not only saves time and fuel but also reduces carbon emissions, making it an environmentally friendly solution.
Another significant aspect of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT is data analytics and reporting. Every action, from bin usage patterns to peak waste generation hours, is recorded and analyzed. This information provides actionable insights that help municipalities and industries plan long-term waste strategies, allocate resources more efficiently, and even encourage recycling programs.
IoT-based smart waste management also supports public engagement and accountability. Citizens can receive alerts about collection schedules, report overflowing bins via mobile apps, and participate actively in maintaining urban cleanliness. By integrating IoT technology, waste management becomes a collaborative, transparent process that benefits both authorities and the community.
Furthermore, these systems contribute to regulatory compliance and public health. By monitoring hazardous, medical, or industrial waste, IoT-enabled solutions ensure proper handling, storage, and disposal according to environmental regulations. This reduces the risk of contamination, disease spread, and other health hazards associated with unmanaged waste.
Key Components of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT
With urban populations growing exponentially, traditional waste management methods are no longer adequate. Increasing amounts of municipal, commercial, and industrial waste require a more intelligent approach. A Smart Waste Management System in IoT leverages Internet of Things (IoT) technology to create a fully connected, data-driven ecosystem that ensures cleaner cities, cost efficiency, and environmental sustainability. To understand how this system works, it’s essential to explore its key components in detail.
1. IoT-Enabled Smart Bins
The backbone of any smart waste management system is the IoT-enabled smart bin. These bins are equipped with sensors that monitor:
- Fill Levels: Using ultrasonic or infrared sensors, bins can detect when they are partially or completely full.
- Weight Monitoring: Load sensors measure the exact weight of the waste inside the bin, which helps in optimizing collection schedules.
- Waste Type Identification: Advanced bins can distinguish between organic, recyclable, and hazardous waste using smart algorithms or AI-powered sensors.
Practical Benefits:
- Prevents bin overflow and littering
- Reduces unnecessary waste collection trips
- Supports recycling programs at the source
2. Sensor Networks
A network of interconnected sensors is essential for real-time monitoring. Key types include:
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Measure the distance between the bin top and waste surface to determine fill levels accurately.
- Infrared Sensors: Detect the presence of specific materials for waste segregation.
- Weight Sensors: Track waste accumulation and prevent overloading.
- Environmental Sensors: Monitor temperature, odor, or hazardous gas emissions, ensuring health and safety compliance.
Importance:
- Provides precise, real-time data for analytics
- Enables predictive waste collection and maintenance
- Ensures health safety in public spaces
3. GPS and Fleet Management Systems
Smart waste collection vehicles are integrated with GPS and IoT tracking systems, enabling:
- Route Optimization: Data from smart bins allows dynamic routing, reducing fuel usage and travel time.
- Real-Time Tracking: Fleet managers can monitor vehicle locations and collection status.
- Operational Efficiency: Ensures vehicles only visit bins that need collection, minimizing unnecessary trips.
Example: A city using GPS-enabled waste trucks can reduce fuel consumption by up to 30% by optimizing routes based on real-time bin data.
4. Cloud-Based Data Analytics Platforms
All the data collected from sensors, bins, and vehicles are transmitted to cloud-based platforms, where it is analyzed using AI and machine learning algorithms. Features include:
- Real-Time Analytics: Identify which areas require immediate attention.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecast waste generation trends and adjust collection schedules.
- Performance Metrics: Track collection efficiency, vehicle performance, and bin usage over time.
Benefits:
- Helps authorities plan better for future resource allocation
- Reduces operational costs by improving efficiency
- Supports long-term urban planning strategies
5. Mobile Applications and Dashboards
A mobile dashboard provides both authorities and citizens with complete visibility into the waste management process. Key features:
- Monitoring bin fill levels and collection schedules
- Reporting overflowing bins or illegal dumping
- Notifying citizens about waste pickup times or recycling initiatives
Impact:
- Encourages citizen participation
- Enhances transparency and accountability
- Strengthens public trust in municipal services
6. Automated Alerts and Notifications
IoT systems send automated notifications to maintenance teams and municipal authorities, such as:
- Full or overflowing bins
- Deviations in vehicle routes
- Equipment malfunctions or sensor failures
Advantages:
- Proactive waste management
- Reduced downtime and operational delays
- Improved public health and sanitation
7. Waste Segregation and Recycling Modules
Modern IoT systems may include modules that sort waste at the source, supporting sustainability goals:
- Organic vs. Non-Organic Waste: Sensors detect food or biodegradable waste.
- Recyclable Waste: Smart systems identify plastics, paper, and metals.
- Hazardous Waste: Detection of potentially harmful materials ensures safe disposal.
Benefits:
- Enhances recycling efficiency
- Reduces landfill waste
- Promotes environmental sustainability
8. Predictive Maintenance Tools
Predictive maintenance is a crucial component for long-term efficiency:
- Sensors track the health of bins, compactors, and vehicles
- Alerts notify when equipment requires maintenance or replacement
- Prevents unexpected breakdowns and ensures uninterrupted waste collection
Impact:
- Reduces maintenance costs
- Improves system reliability
- Extends the lifespan of equipment
9. Energy-Efficient and Sustainable Design
Energy efficiency is a key focus in IoT-based waste management:
- Solar-Powered Smart Bins: Reduce dependency on electricity.
- Fuel-Efficient Collection Vehicles: Minimize emissions.
- Low-Energy Sensors: Ensure continuous operation without heavy power consumption.
Outcome:
- Supports green initiatives
- Reduces carbon footprint
- Aligns with smart city sustainability goals
Benefits of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT
With the rise of urbanization and industrial activity, waste generation is growing exponentially. Traditional waste management methods struggle to keep up with the increasing volumes, often leading to overflowing bins, environmental pollution, and high operational costs. Implementing a Smart Waste Management System in IoT transforms the way cities and organizations handle waste, making the process efficient, sustainable, and data-driven.
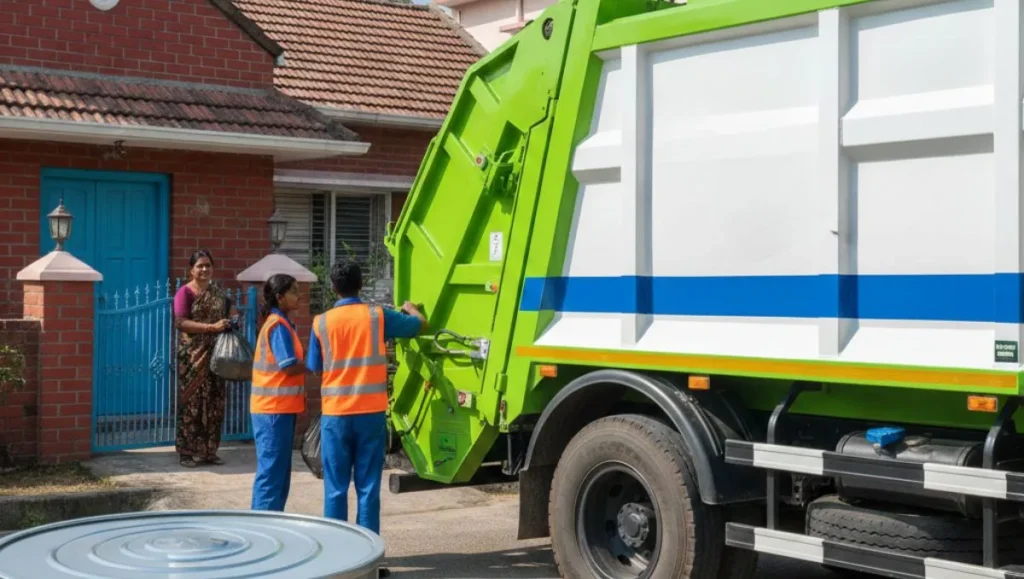

By integrating IoT sensors, cloud analytics, mobile applications, and GPS-enabled fleet management, smart waste systems offer numerous advantages that go beyond conventional collection methods. Below is a detailed explanation of the key benefits:
1. Real-Time Waste Monitoring
IoT-enabled bins are equipped with advanced sensors that continuously monitor fill levels, weight, and sometimes the type of waste.
Detailed Explanation:
- Ultrasonic and infrared sensors detect how full a bin is, sending real-time alerts to central monitoring systems.
- Weight sensors provide additional data to prevent overloading and optimize vehicle schedules.
- Some advanced bins can detect waste types, supporting segregation at the source.
Impact:
- Reduces littering and prevents overflowing bins in public areas
- Ensures timely collection, enhancing urban cleanliness
- Helps authorities allocate resources more efficiently based on real-time data
Example: A smart city in Europe reduced bin overflow complaints by 70% after installing IoT-enabled bins in public areas.
2. Optimized Waste Collection Routes
By integrating IoT sensor data with GPS-enabled collection vehicles, waste collection can be optimized based on actual demand rather than fixed schedules.
Detailed Explanation:
- Real-time data from bins allows fleet management systems to prioritize collection routes where bins are near full capacity.
- Dynamic route planning minimizes fuel consumption, reduces traffic congestion, and ensures faster service.
Impact:
- Reduces unnecessary vehicle trips, lowering operational costs and carbon emissions
- Saves time for waste collection teams, allowing better resource allocation
- Ensures high-priority areas, such as hospitals or commercial zones, are serviced promptly
Example: Cities implementing dynamic route optimization reported a 30–40% reduction in fuel costs.
3. Cost Efficiency
Smart waste management systems reduce operational and maintenance expenses significantly.
Detailed Explanation:
- Optimized collection schedules lower labor costs by reducing unnecessary trips.
- Predictive maintenance alerts prevent costly breakdowns of bins, compactors, and vehicles.
- Reduced fuel consumption and wear-and-tear on collection vehicles lower long-term costs.
Impact:
- Makes large-scale waste management financially sustainable
- Ensures budget allocation can be focused on infrastructure and sustainability initiatives
Example: An Indian city using IoT-based waste management saved over 25% on fuel and labor costs within the first year of implementation.
4. Environmental Sustainability
A Smart Waste Management System in IoT significantly reduces environmental impact by enabling greener operations.
Detailed Explanation:
- Optimized vehicle routes reduce fuel consumption, lowering CO₂ emissions.
- Smart segregation modules increase recycling efficiency and reduce landfill usage.
- Sensors detect hazardous waste and prevent contamination of soil and water sources.
Impact:
- Promotes sustainable urban environments
- Helps cities comply with environmental regulations
- Supports global goals for reducing carbon footprints
Example: Cities with IoT-based recycling programs reported a 50% increase in recyclable material recovery.
5. Improved Public Health and Safety
Unmanaged waste poses serious health hazards, including pest infestations, disease spread, and air pollution.
Detailed Explanation:
- Real-time monitoring prevents overflowing bins, reducing breeding grounds for bacteria and insects.
- Hazardous waste detection ensures safe handling of toxic materials.
- Alerts enable rapid response to sanitation issues, especially in high-risk zones like hospitals.
Impact:
- Enhances community health standards
- Reduces odor and environmental hazards in urban areas
- Minimizes public complaints related to sanitation
Example: Cities implementing IoT smart waste bins saw a measurable decline in reported hygiene-related complaints.
6. Data-Driven Decision Making
IoT waste systems generate vast amounts of data that can be leveraged for strategic planning.
Detailed Explanation:
- Data analytics identifies peak waste generation hours, high-density areas, and underutilized resources.
- Predictive models forecast future waste generation trends for better scheduling and infrastructure planning.
- Authorities can track performance metrics like collection efficiency, vehicle utilization, and bin usage.
Impact:
- Supports proactive waste management instead of reactive methods
- Enables informed policymaking and long-term urban planning
- Facilitates continuous improvement of waste management strategies
Example: A smart city used IoT data to identify neighborhoods with high waste generation and implemented targeted recycling initiatives, increasing recycling rates by 35%.
7. Predictive Maintenance
Smart sensors monitor the condition of bins, compactors, and collection vehicles.
Detailed Explanation:
- Sensors detect wear-and-tear or potential malfunctions before equipment failure occurs.
- Automated alerts notify maintenance teams, allowing preemptive repairs.
Impact:
- Reduces downtime and emergency maintenance costs
- Ensures uninterrupted waste collection operations
- Extends the life of equipment and infrastructure
Example: Predictive maintenance in smart bins prevented 20% of service interruptions in a European city.
8. Citizen Engagement and Transparency
IoT-based systems enhance transparency by keeping citizens informed and engaged.
Detailed Explanation:
- Mobile apps provide real-time updates on collection schedules and bin statuses.
- Citizens can report overflowing bins, illegal dumping, or other sanitation issues.
- Communities are educated about recycling and proper waste disposal.
Impact:
- Encourages active participation in urban cleanliness
- Builds public trust in municipal services
- Promotes a culture of responsibility and sustainability
Example: Cities with citizen-facing mobile apps saw higher compliance with waste segregation and recycling programs.
9. Scalability and Flexibility
IoT-based waste management systems are highly adaptable and scalable.
Detailed Explanation:
- Can be deployed in small towns, large cities, industrial zones, airports, and commercial complexes.
- Modular design allows incremental expansion as urban areas grow or as technology improves.
- Integrates seamlessly with other smart city initiatives like traffic management and energy-efficient systems.
Impact:
- Future-proof solution for growing urban populations
- Flexible enough to support multiple sectors, from municipalities to private organizations
- Aligns with smart city and sustainability goals
10. Regulatory Compliance
Smart waste systems help industries and cities comply with environmental regulations.
Detailed Explanation:
- Automated reports track hazardous and industrial waste disposal accurately.
- Detailed analytics demonstrate adherence to local, national, and international environmental laws.
- Prevents penalties or legal issues related to improper waste disposal.
Impact:
- Ensures safe handling of hazardous waste
- Supports sustainability and eco-friendly practices
- Enhances credibility and public trust in municipal or industrial waste operations
Applications of Smart Waste Management System in IoT
As urban populations expand and industrial activity accelerates, traditional waste management approaches are no longer sufficient. Inefficient collection, improper disposal, and lack of monitoring lead to environmental pollution, public health risks, and high operational costs. A Smart Waste Management System in IoT addresses these challenges by integrating Internet of Things (IoT) technology into every stage of waste management. Beyond its operational efficiency, this technology has numerous applications across municipal, industrial, and commercial environments.
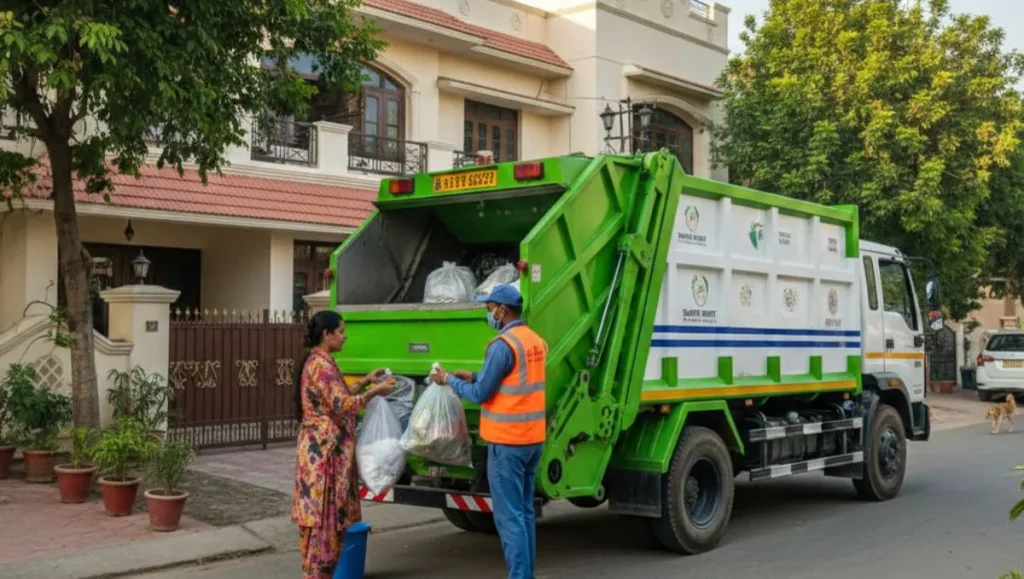

1. Municipal Solid Waste Management
The most common application of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT is in municipal solid waste (MSW) management.
How it Works:
- Smart bins with IoT sensors monitor fill levels and send data to a centralized dashboard.
- GPS-enabled collection vehicles optimize routes based on real-time bin data.
- Analytics platforms help municipalities plan resource allocation and predict waste generation patterns.
Benefits:
- Prevents overflowing bins and littered streets
- Reduces operational costs through optimized routes and schedules
- Enhances urban cleanliness and public health
Example: Many European cities have successfully implemented smart bins and IoT-enabled waste trucks, reducing collection costs by up to 30%.
2. Industrial Waste Monitoring
Industries produce large volumes of hazardous, chemical, or recyclable waste. IoT-enabled systems help track, manage, and dispose of this waste responsibly.
How it Works:
- Sensors monitor industrial waste storage containers and track fill levels.
- Hazardous or toxic waste is identified and flagged for special handling.
- Data is collected for regulatory compliance reporting.
Benefits:
- Ensures safe handling of hazardous materials
- Reduces the risk of environmental contamination
- Helps industries comply with local and international environmental regulations
Example: Manufacturing plants using IoT smart waste solutions can prevent accidental chemical spills by monitoring hazardous waste in real-time.
3. Smart City Initiatives
A Smart Waste Management System in IoT is an integral part of broader smart city initiatives.
How it Works:
- Waste collection is integrated with other smart systems such as traffic, lighting, and energy management.
- Data from IoT sensors is analyzed alongside city-wide infrastructure to optimize urban planning.
Benefits:
- Enhances operational efficiency across municipal services
- Reduces environmental impact and carbon footprint
- Promotes sustainable urban living
Example: In smart cities like Singapore and Barcelona, IoT-enabled waste systems are combined with traffic and environmental monitoring to streamline urban services.
4. Recycling Programs
IoT-based waste systems play a vital role in promoting recycling.
How it Works:
- Smart bins with waste segregation sensors separate organic, recyclable, and non-recyclable waste.
- Data analytics monitor recycling performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Citizens can receive notifications and guidance on proper disposal.
Benefits:
- Increases recycling efficiency and reduces landfill waste
- Encourages community participation in sustainability programs
- Tracks and improves the success of municipal recycling initiatives
Example: Cities using IoT-enabled recycling bins have seen up to a 50% increase in recyclables collected from public areas.
5. Healthcare and Hospital Waste Management
Hospitals generate biohazardous and medical waste that requires careful monitoring and disposal.
How it Works:
- IoT-enabled bins detect fill levels and waste type (biohazardous, sharps, or general medical waste).
- Alerts notify staff when collection is needed or if improper disposal occurs.
- Data supports compliance with health and safety regulations.
Benefits:
- Reduces risk of infections and contamination
- Ensures timely and safe collection of medical waste
- Supports regulatory compliance and auditing
Example: Hospitals implementing smart medical waste bins reduce manual monitoring efforts and improve safety for staff and patients.
6. Airports, Railway Stations, and Commercial Complexes
High-footfall areas require efficient and scalable waste management solutions.
How it Works:
- Smart bins are installed throughout terminals or complexes.
- IoT sensors provide real-time fill-level data to central management systems.
- Collection routes are dynamically optimized to match traffic flow and occupancy.
Benefits:
- Maintains cleanliness in high-traffic zones
- Reduces operational costs for large facilities
- Enhances customer experience and public perception
Example: Airports in major cities like Dubai and Amsterdam have deployed smart bins, improving waste collection efficiency by 40–50%.
7. Event Management and Public Gatherings
Temporary events, festivals, or concerts generate large amounts of waste in short periods.
How it Works:
- Portable smart bins track waste accumulation during events.
- Real-time data alerts staff to bins nearing capacity.
- Collection teams can be deployed dynamically based on actual demand.
Benefits:
- Prevents overflowing bins in crowded events
- Reduces environmental impact after events
- Supports sustainability initiatives for large gatherings
Example: Music festivals and sports events using IoT smart bins ensure cleaner venues and reduced post-event waste cleanup costs.
8. Industrial Parks and Large Manufacturing Zones
Large industrial zones produce both municipal and industrial waste.
How it Works:
- Sensors track multiple bins across the industrial area.
- Predictive analytics help schedule collection without disrupting operations.
- Waste segregation sensors ensure recyclables are separated from hazardous materials.
Benefits:
- Enhances operational efficiency in industrial zones
- Reduces environmental risks and landfill dependency
- Supports sustainability goals for industrial operations
Example: Industrial parks in India and Europe have implemented IoT-based waste monitoring to manage thousands of bins efficiently, reducing waste-related complaints.
ANS IT India Provide Smart Waste Management System in IoT Solution
In today’s rapidly growing urban landscape, effective waste management is one of the biggest challenges for cities and industries. Traditional collection methods often lead to overflowing bins, inefficient routes, high operational costs, and environmental pollution. To solve these issues, ANS IT India offers an advanced Smart Waste Management System in IoT designed to make waste collection smarter, faster, and more efficient.
A Smart Waste Management System in IoT uses connected sensors, real-time monitoring, cloud-based software, and intelligent analytics to transform how waste is managed. ANS IT India combines innovative IoT technology with practical implementation strategies to help municipalities, commercial complexes, industries, and smart cities achieve sustainable waste management.
What ANS IT India Offers in Smart Waste Management System in IoT
ANS IT India provides a complete end-to-end Smart Waste Management System in IoT solution that includes hardware, software, installation, and ongoing technical support.
1. Smart Bin Sensors
The solution includes IoT-enabled sensors installed inside waste bins to monitor:
- Fill level status
- Temperature changes
- Movement or tampering
- Moisture levels (if required)
These sensors send real-time data to a centralized cloud platform, ensuring authorities are always aware of the bin status.
2. Real-Time Monitoring Dashboard
ANS IT India provides a powerful web-based dashboard that allows users to:
- Monitor bin status live
- Track collection vehicle movement
- View alerts for full or damaged bins
- Analyze waste data through reports
The centralized control system helps organizations make faster and more informed decisions.
3. Route Optimization for Waste Collection
The Smart Waste Management System in IoT from ANS IT India uses intelligent route planning to:
- Reduce fuel consumption
- Avoid unnecessary trips
- Optimize manpower usage
- Improve collection efficiency
By collecting waste only when bins are full, organizations can significantly cut operational costs.
4. Automated Alerts & Notifications
The system automatically generates alerts when:
- A bin reaches maximum capacity
- A fire risk or abnormal temperature is detected
- Unauthorized movement occurs
- Scheduled collection is delayed
These smart alerts improve response time and prevent health hazards.
5. Data Analytics & Reporting
ANS IT India’s Smart Waste Management System in IoT provides advanced analytics that help in:
- Identifying high-waste zones
- Tracking waste generation trends
- Measuring recycling performance
- Planning resource allocation
Data-driven insights enable better long-term planning and regulatory compliance.
6. Smart City Integration
The solution can be integrated with:
- Smart traffic systems
- Environmental monitoring platforms
- Urban governance dashboards
- Public complaint management systems
This makes ANS IT India’s Smart Waste Management System in IoT ideal for smart city projects across India.
Benefits of Choosing ANS IT India
✔ Cost-Effective Implementation
The system reduces fuel costs, labor expenses, and unnecessary maintenance.
✔ Scalable and Flexible
Suitable for municipalities, residential societies, commercial complexes, hospitals, campuses, and industries.
✔ Improved Environmental Impact
Better waste segregation and optimized collection reduce landfill waste and carbon emissions.
✔ Enhanced Public Health
Prevents overflow situations and supports cleaner surroundings.
✔ Reliable Technical Support
ANS IT India provides professional installation, maintenance, and customer support to ensure smooth operations.
Why Smart Waste Management System in IoT is the Future
As cities grow and waste production increases, adopting a Smart Waste Management System in IoT is essential. Governments and private organizations must move toward automation and digital monitoring to improve efficiency and sustainability.
ANS IT India is committed to delivering smart, reliable, and scalable waste management solutions that align with modern environmental goals. By leveraging IoT technology, they help organizations transition from reactive waste collection to proactive waste management.
Future of Smart Waste Management System in IoT
As cities expand and global waste generation continues to rise, traditional waste collection and disposal methods are becoming increasingly inefficient and environmentally unsustainable. The Smart Waste Management System in IoT is already transforming urban sanitation by introducing real-time monitoring, automation, and data-driven decision-making. However, the future of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT goes far beyond basic smart bins and route optimization. It is evolving into an intelligent, fully integrated ecosystem that will redefine how cities manage waste in the coming decades.
1. AI-Powered Predictive Waste Management
The future of the Smart Waste Management System in IoT will heavily rely on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
What to Expect:
- AI algorithms will predict waste generation patterns based on historical data, weather conditions, festivals, and population density.
- Automated systems will adjust collection schedules dynamically without manual intervention.
- Smart analytics will identify areas with high waste generation and recommend preventive measures.
Impact:
- Reduced operational costs
- Improved efficiency in waste collection
- Data-driven urban planning
Predictive intelligence will shift waste management from a reactive system to a proactive one.
2. Advanced Robotics and Automated Segregation
One of the biggest challenges in waste management is proper segregation. The future will see robotics integrated with IoT systems.
Innovations Ahead:
- Robotic arms powered by AI for automated sorting in recycling plants
- Computer vision systems that identify plastics, metals, paper, and organic waste
- Smart compactors that compress waste automatically for efficient storage and transport
Benefits:
- Increased recycling rates
- Reduced human exposure to hazardous waste
- Improved operational speed and accuracy
This advancement will significantly enhance recycling efficiency and reduce landfill dependency.
3. Integration with Smart City Infrastructure
The Smart Waste Management System in IoT will become a core component of smart city ecosystems.
Future Integration:
- Connected with smart traffic systems to avoid congestion during waste collection
- Integrated with environmental monitoring sensors to track pollution levels
- Linked with smart energy grids for sustainable power usage
Result:
- Seamless coordination between city departments
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Holistic urban management
Waste management will no longer operate independently but as part of a unified smart city platform.
4. Blockchain for Transparency and Compliance
In the future, blockchain technology may be integrated into IoT waste systems.
How It Helps:
- Secure tracking of waste disposal and recycling processes
- Transparent reporting for regulatory compliance
- Prevention of illegal dumping and data manipulation
Outcome:
- Increased accountability
- Better compliance with environmental regulations
- Trust between municipalities, industries, and citizens
Blockchain integration will bring reliability and transparency to waste management operations.
5. Sustainable and Green Innovations
The future of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT aligns closely with sustainability goals.
Emerging Trends:
- Solar-powered smart bins
- Electric or autonomous waste collection vehicles
- Waste-to-energy conversion systems integrated with IoT monitoring
Environmental Benefits:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Energy generation from organic waste
- Support for circular economy models
Smart waste systems will not just manage waste but convert it into valuable resources.
6. Real-Time Citizen Engagement Platforms
Future IoT waste systems will increase citizen participation through advanced mobile platforms.
Expected Features:
- Real-time notifications about recycling programs
- Reward systems for responsible waste disposal
- Gamification to encourage community participation
Impact:
- Stronger civic responsibility
- Increased recycling rates
- Cleaner neighborhoods
Technology will empower communities to actively contribute to waste management efforts.
7. Autonomous and Smart Collection Vehicles
Self-driving waste collection vehicles may become a reality.
Future Developments:
- Autonomous trucks guided by IoT data
- Automated waste pickup using robotic arms
- Reduced dependency on manual labor
Benefits:
- Enhanced safety
- Lower operational costs
- Improved efficiency
Automation will streamline collection processes and reduce human intervention in high-risk environments.
8. Big Data and Hyper-Personalized Waste Solutions
With massive data collection capabilities, future systems will offer hyper-local insights.
What This Means:
- Area-specific waste management strategies
- Personalized recycling guidelines for neighborhoods
- Improved planning for residential and industrial zones
Advantage:
- Optimized resource allocation
- Targeted awareness campaigns
- More efficient waste reduction programs
Big data will allow cities to tailor waste solutions according to local needs.
9. Global Standardization and Expansion
As IoT adoption increases worldwide, standardized frameworks for smart waste management will emerge.
Expected Outcomes:
- International best practices
- Scalable models for developing countries
- Cross-border environmental cooperation
This will accelerate global adoption of the Smart Waste Management System in IoT, making sustainable waste solutions accessible worldwide.
Conclusion: Smart Waste Management System in IoT
The Smart Waste Management System in IoT represents a powerful transformation in how modern cities, businesses, and communities handle waste. In an era where rapid urbanization and environmental challenges are increasing, traditional waste collection methods are no longer sufficient. The Smart Waste Management System in IoT provides a data-driven, automated, and sustainable approach that ensures efficiency, transparency, and long-term environmental protection.
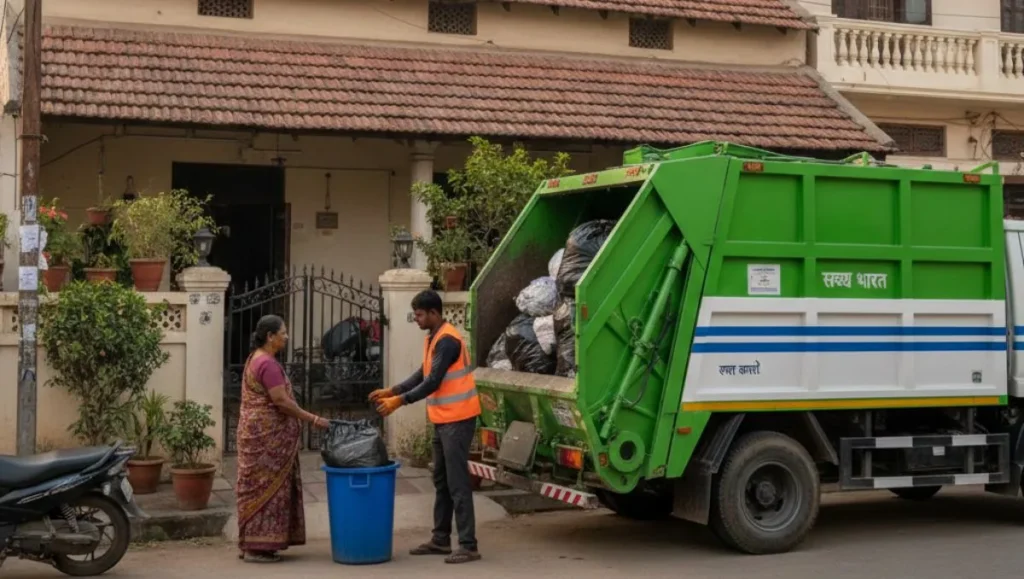

At its core, a Smart Waste Management System in IoT combines smart sensors, real-time data analytics, cloud platforms, and connected devices to monitor waste levels, optimize collection routes, and improve recycling processes. This intelligent system reduces operational costs, minimizes fuel consumption, and lowers carbon emissions. By collecting accurate data from waste bins and processing units, municipalities can make informed decisions and allocate resources more effectively.
One of the biggest advantages of a Smart Waste Management System in IoT is its ability to support sustainability goals. By promoting better waste segregation, recycling efficiency, and waste-to-energy initiatives, it helps reduce landfill dependency. This not only protects the environment but also supports the circular economy by encouraging resource reuse and responsible disposal practices.
From a business perspective, companies benefit through improved cost predictability, reduced manpower requirements, and enhanced operational visibility. Real-time alerts prevent overflow situations, while predictive analytics ensure timely maintenance of equipment and vehicles. Over time, this leads to higher efficiency and better service quality.
Moreover, the Smart Waste Management System in IoT strengthens public health and safety. Proper waste monitoring reduces the risk of disease spread, prevents environmental contamination, and ensures regulatory compliance. Citizens also become active participants through mobile apps and awareness programs, creating a more responsible and environmentally conscious society.
Looking ahead, the Smart Waste Management System in IoT will continue to evolve with advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, 5G connectivity, and smart city integration. These innovations will make waste management even more proactive, automated, and scalable.
In conclusion, adopting a Smart Waste Management System in IoT is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern urban development. It delivers economic, environmental, and social benefits while paving the way for cleaner cities and a sustainable future. Organizations and governments that invest in this smart solution today will lead the transformation toward a greener tomorrow.